Pathophysiology Of Pulmonary Embolism
A blood clot dislodges and is swept into the pulmonary circulation and lodges in. A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that occurs in the lungs.
 Ppt Pulmonary Embolism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
Ppt Pulmonary Embolism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
Pulmonary embolism can be difficult to diagnose especially in people who have underlying heart or lung disease.
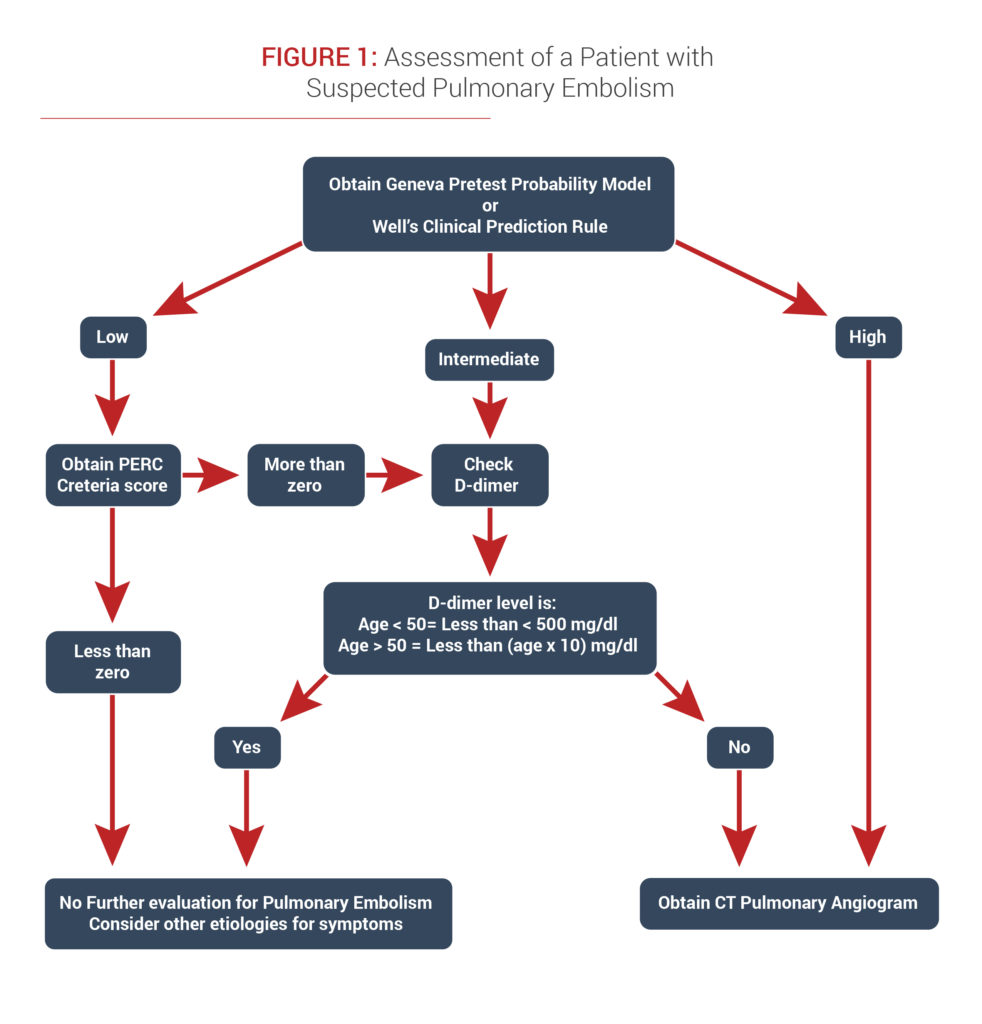
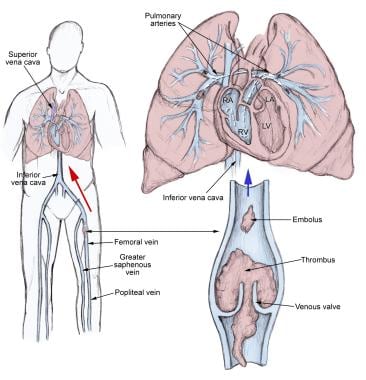
Pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism is the occlusion of pulmonary arteries by thrombi that originate elsewhere typically in the large veins of the legs or pelvis. A pulmonary embolism pe happens when a blood clot gets caught in an artery in the lungs. Evidence of leg dvt is found in about 70 of patients who have sustained a pulmonary embolism.
To reach the lungs thromboemboli travel through the right side of the. The pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism. It is commonly caused by a venous thrombus that has dislodged from its site of formation and embolized to the arterial blood supply of one of the lungs.
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs. In most of the remainder it is assumed that the whole thrombus has. Deep venous thrombosis dvt and pulmonary embolism are therefore parts of the same process venous thromboembolism.
For that reason your doctor will likely discuss your medical history do a physical exam and order one or more of the following tests. National center for biotechnology information. Although pulmonary embolism can arise from anywhere in the body most commonly it arises from the calf veins.
In most cases pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from deep veins in the legs or rarely from veins in other parts of the body deep vein thrombosis. Pulmonary embolism pe occurs when there is an acute obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches. Pulmonary emboli often arise from thrombi originating in the deep venous system of the lower extremities or pelvis.
Risk factors for pulmonary embolism are conditions that impair venous return conditions that cause endothelial injury or dysfunction and underlying hypercoagulable states. This blockage can cause serious problems like lung damage low oxygen levels and even death. The venous thrombi predominately originate in venous valve pockets inset and at other sites of presumed venous stasis.
Thrombotic pulmonary embolism is not an isolated disease of the chest but a complication of venous thrombosis. It can damage part of the lung due to restricted blood flow decrease oxygen levels in the blood and affect other organs as well.
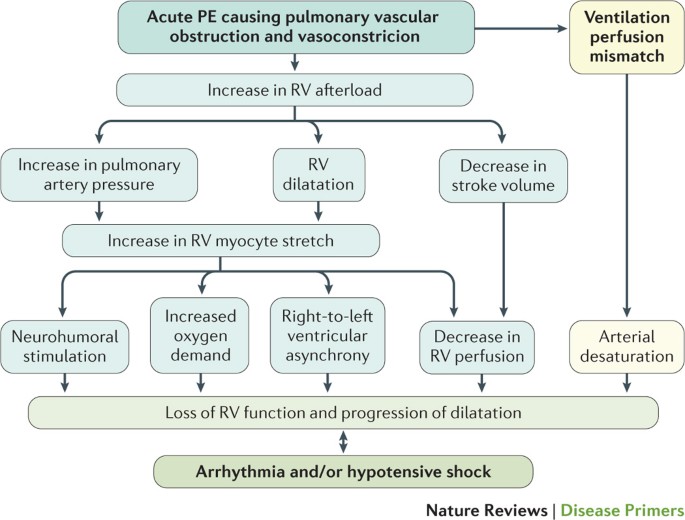 Pulmonary Embolism Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Pulmonary Embolism Nature Reviews Disease Primers
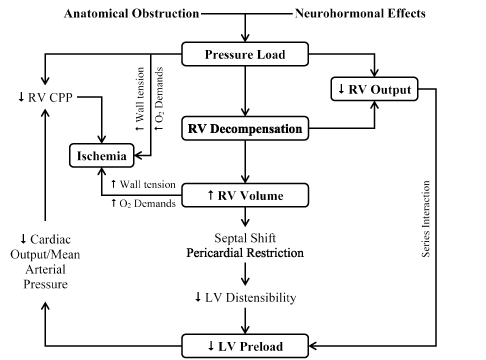 Massive Pulmonary Embolism Heart Failure A Review Of Clinical
Massive Pulmonary Embolism Heart Failure A Review Of Clinical
Complications Of Pulmonary Embolism Calgary Guide
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
Acute Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
 Venous Thromboembolism Risk Factors Assessment Prevention
Venous Thromboembolism Risk Factors Assessment Prevention
 Figure 1 From Management Of Submassive Pulmonary Embolism
Figure 1 From Management Of Submassive Pulmonary Embolism
Pathophysiology Of Pulmonary Embolism Mcmaster Pathophysiology
Pulmonary Embolism Pathogenesis And Laboratory Findings Calgary
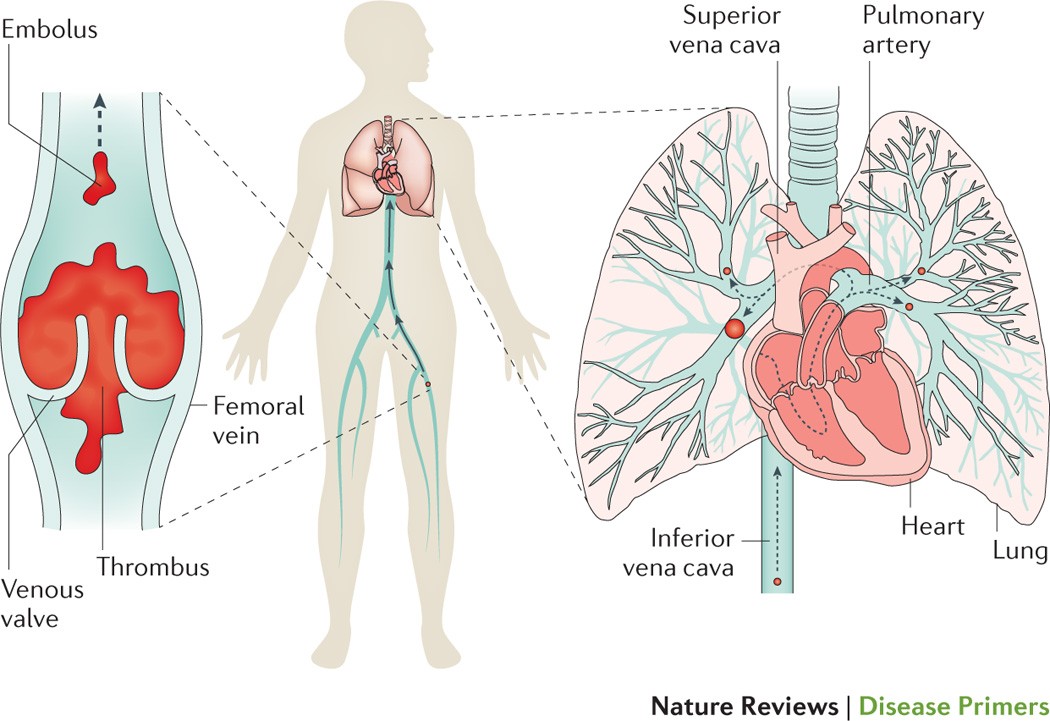 Pulmonary Embolism Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Pulmonary Embolism Nature Reviews Disease Primers
 Signs And Symptoms Of Pulmonary Embolism Calgary Guide
Signs And Symptoms Of Pulmonary Embolism Calgary Guide
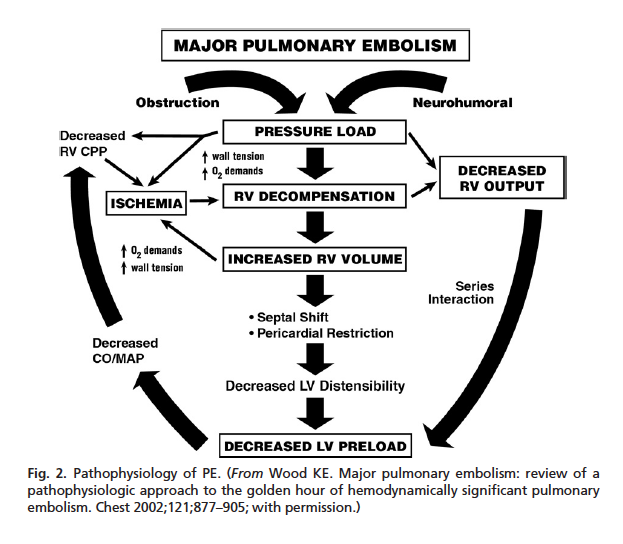 Hemodynamically Unstable Pulmonary Embolism Core Em
Hemodynamically Unstable Pulmonary Embolism Core Em
 Pathophysiology Of Hemodynamic Instability Due To Pe Rv Right
Pathophysiology Of Hemodynamic Instability Due To Pe Rv Right
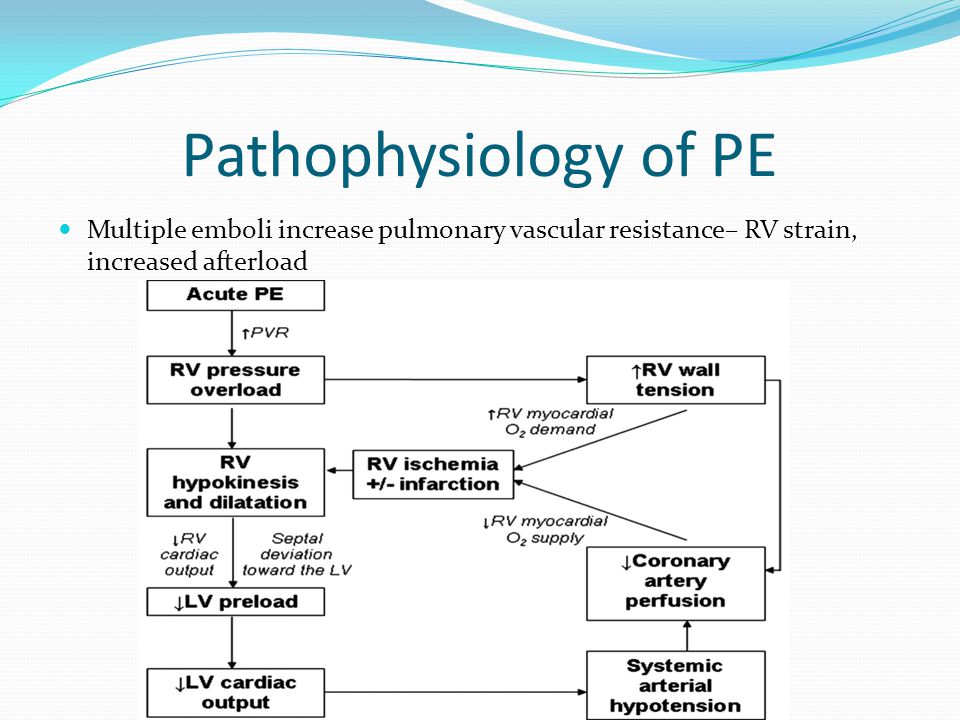
 Pathophysiologic Cycle Of High Risk Pe Pe Pulmonary Embolism Pa
Pathophysiologic Cycle Of High Risk Pe Pe Pulmonary Embolism Pa
 Pulmonary Embolism Pe Pulmonary Disorders Merck Manuals
Pulmonary Embolism Pe Pulmonary Disorders Merck Manuals
 Pdf Pulmonary Embolism Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment
Pdf Pulmonary Embolism Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcrlqpbi4xdcdpy3ghmzw Jkpi2fl5xr31kkc4ofgut1kwae Bsd Usqp Cau
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
Acute Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
Pulmonary Embolism Armando Hasudungan

 Flow Chart The Society For Vascular Medicine
Flow Chart The Society For Vascular Medicine
 Nonthrombotic Pulmonary Embolism Air Amniotic Fluid Fat Tumor
Nonthrombotic Pulmonary Embolism Air Amniotic Fluid Fat Tumor
 Major Pulmonary Embolism Review Of A Pathophysiologic Approach To
Major Pulmonary Embolism Review Of A Pathophysiologic Approach To
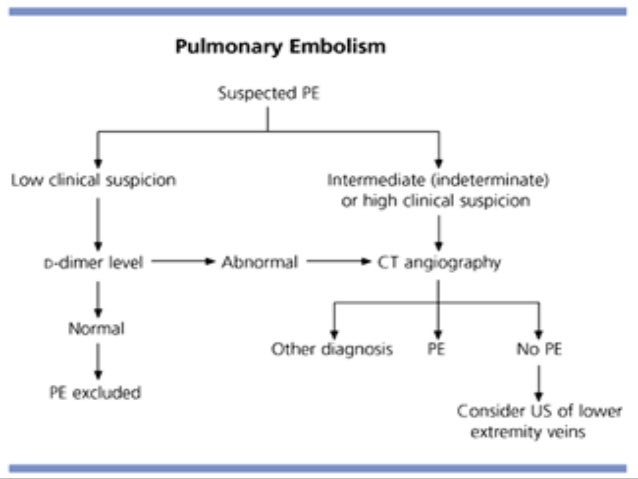 Thromboembolism Pulmonary Embolism General Pathology
Thromboembolism Pulmonary Embolism General Pathology
 Pulmonary Embolism Part I Overview Youtube
Pulmonary Embolism Part I Overview Youtube
 Nonthrombotic Pulmonary Embolism European Respiratory Society
Nonthrombotic Pulmonary Embolism European Respiratory Society
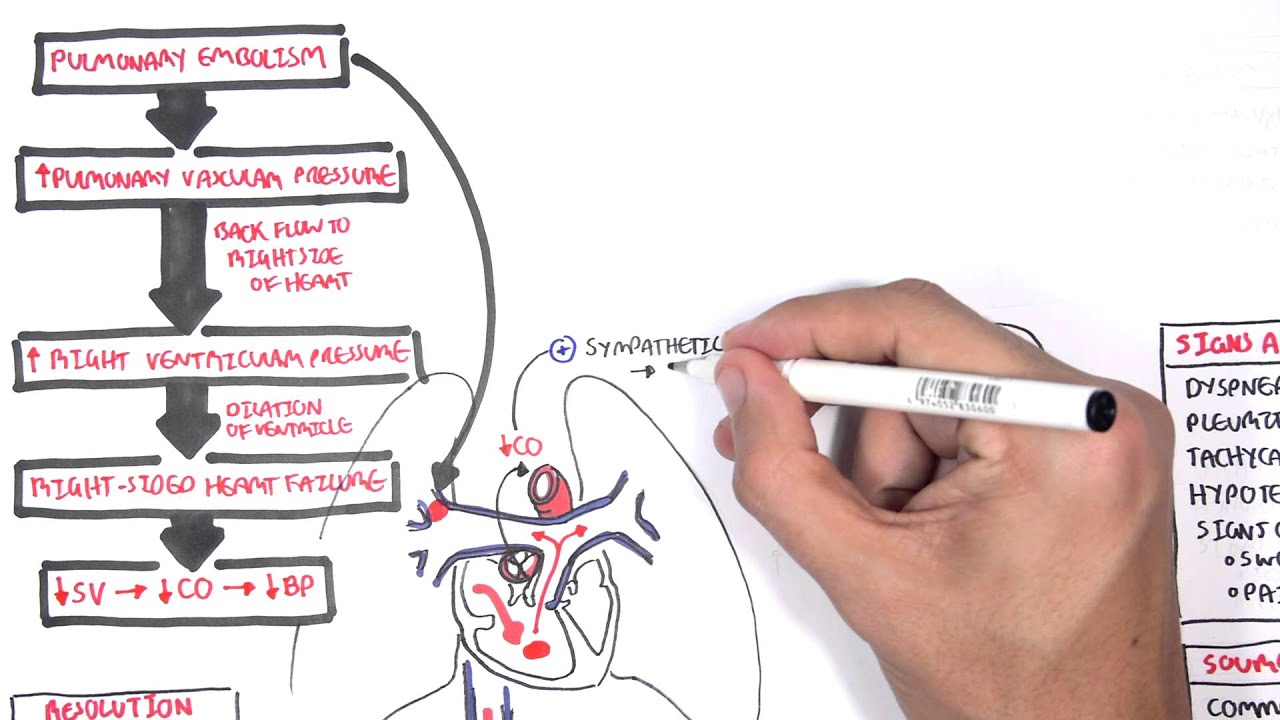 Pulmonary Embolism Part I Overview Youtube
Pulmonary Embolism Part I Overview Youtube
Pulmonary Embolism Armando Hasudungan
 Pulmonary Embolism Pathophysiology Nursing Youtubers Ideas Of
Pulmonary Embolism Pathophysiology Nursing Youtubers Ideas Of
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
Acute Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
 Cteph Pathophysiology Healthcare Professionals
Cteph Pathophysiology Healthcare Professionals
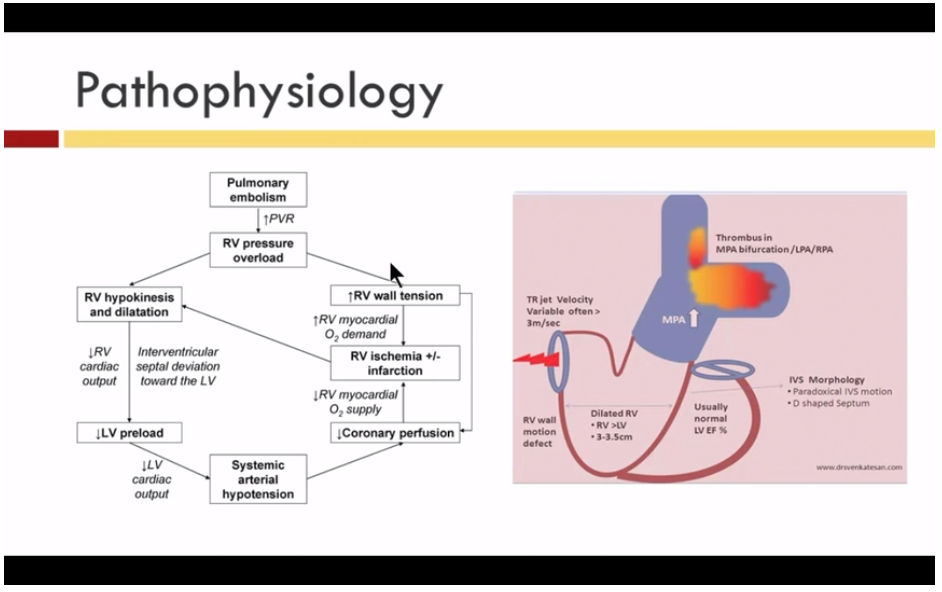 Dr Kon Va Ecmo For Massive Pulmonary Embolism From The Maryland
Dr Kon Va Ecmo For Massive Pulmonary Embolism From The Maryland
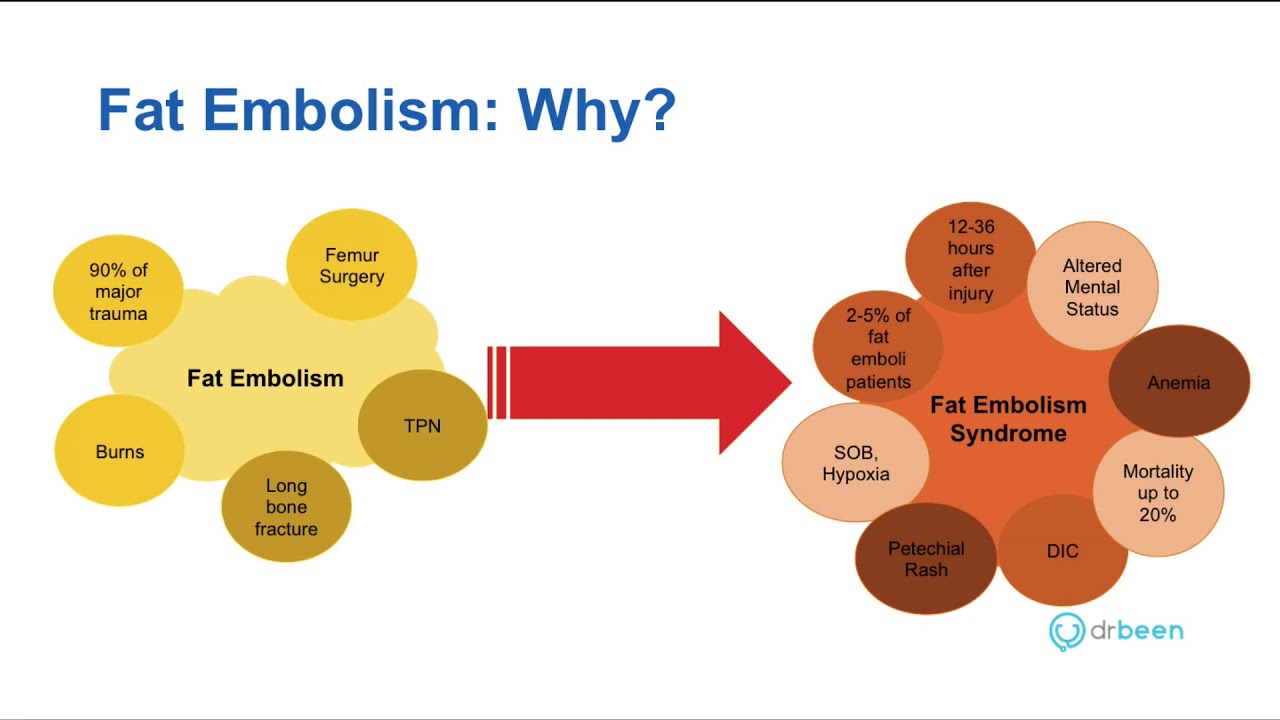 Pathophysiology Of Pulmonary Embolism Youtube
Pathophysiology Of Pulmonary Embolism Youtube
 Management Of Submassive Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
Management Of Submassive Pulmonary Embolism Circulation
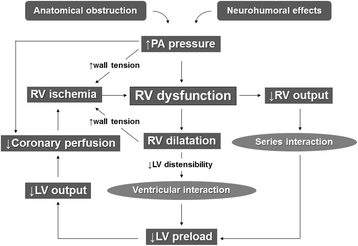 Management Of Patients With High Risk Pulmonary Embolism A
Management Of Patients With High Risk Pulmonary Embolism A
 The Pathophysiology Of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary
The Pathophysiology Of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary
 Pulmonary Embolism Pe Practice Essentials Background Anatomy
Pulmonary Embolism Pe Practice Essentials Background Anatomy
 Pathophysiology Pulmonary Embolism
Pathophysiology Pulmonary Embolism

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar