Dna And Rna Are Both Organic Molecules Called
Deoxyribonucleic acid ribonucleic acid dna rna dna and rna are both examples of made of linked monomers called the instructions in these molecules are used to make. Considered to be lipids.
 Nucleotide Definition Structure 3 Parts Examples Function
Nucleotide Definition Structure 3 Parts Examples Function
Has a polymer of nucleotides.
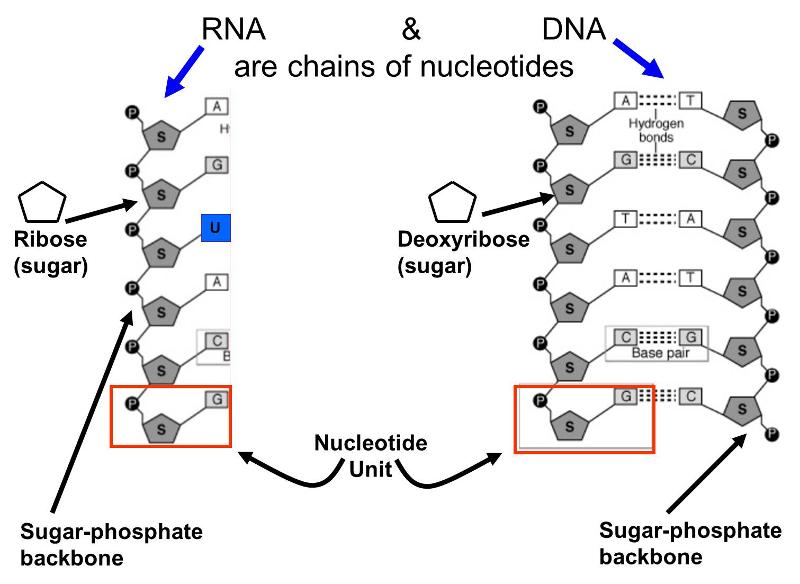
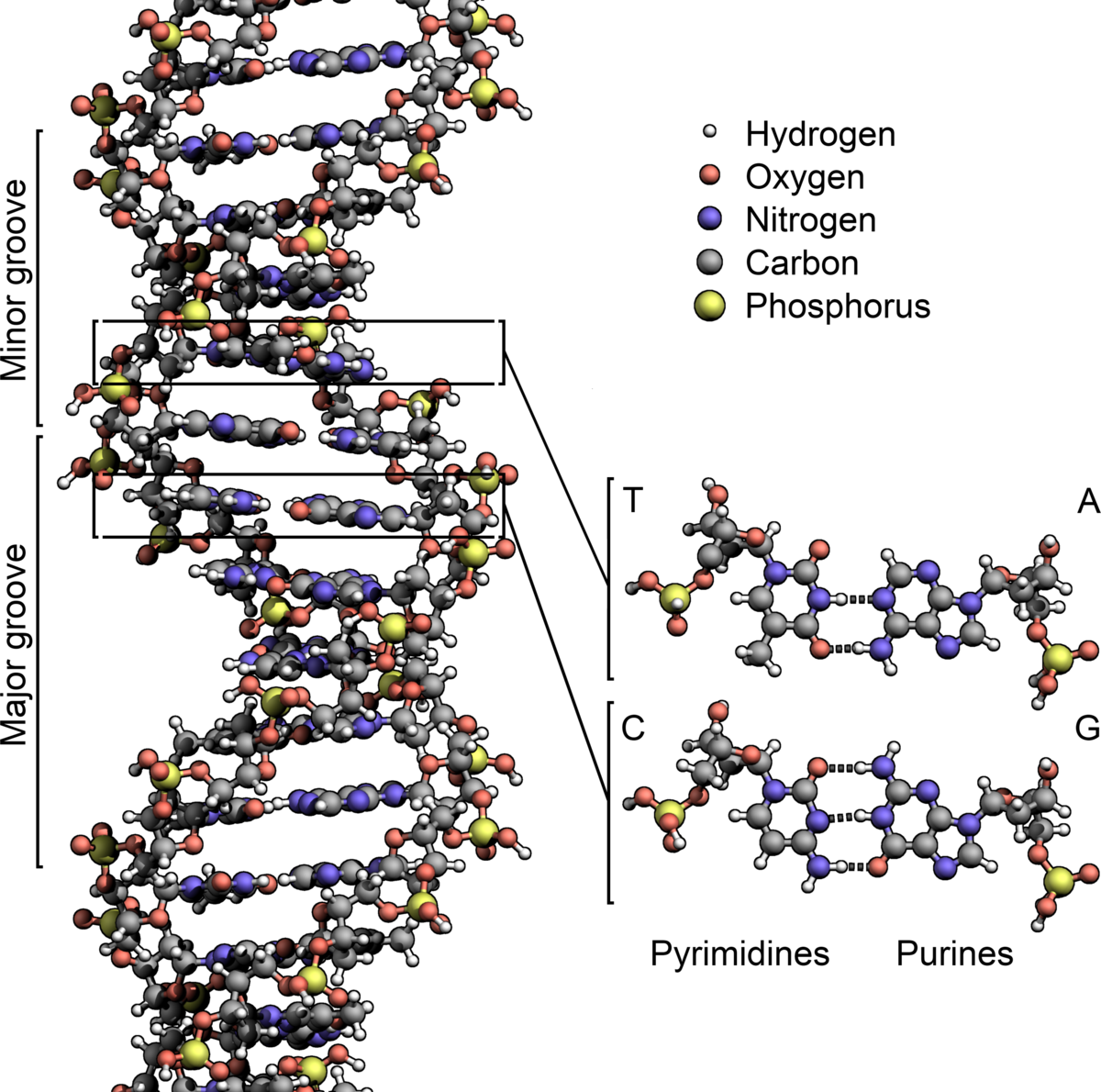
Dna and rna are both organic molecules called. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers deoxyribonucleic acid dna and ribonucleic acid rna both of which are essential biomolecules within all life forms on earth. Dna and rna are both part of a group of molecules known as and are made up of subunits called. Dna has a twisted ladder like form while rna has many different shapes depending on its function.
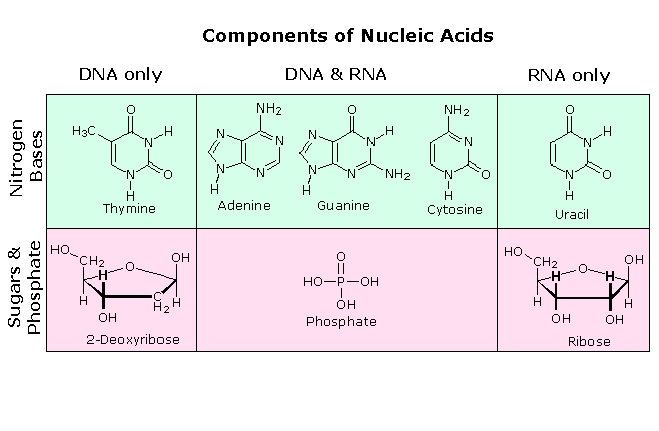
Deoxyribonucleic acid dna and ribonucleic acid rna are the two nucleic acids found in nature. Explore more about types of biomolecules byju s. Both dna and rna are polymers consisting of long linear molecules assembled by polymerase enzymes from repeating structural units or monomers of mononucleotides.
Dna typically remains within the center or nucleus of a cell. Nucleic acids in turn represent one of the four molecules of life or biomolecules. Give the name abbreviation for 2 nucleic acids found in cells.
When bacteria are exposed to nutrient poor conditions they form thick walled structures that contain the chromosome and a small amount of cytoplasm. Sequencing of proteins dna and rna. Biomolecules also called the biological compounds are synthesised by the cell of the living organisms.
Rna can travel throughout the cell to where it is needed. Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. Rearrange and split organic molecules are collectively called.
Due to their different size and complexity eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have slightly different processes during dna replication. 2 double stranded molecules exactly like the original dna are made each with one old new strand semi conservative one old one new strand. Nucleic acid nucleotides protein.
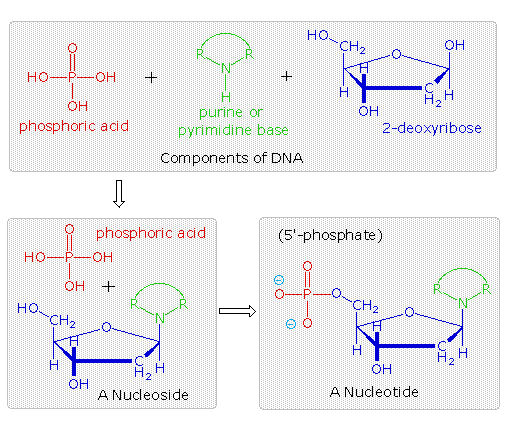
The equal sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. The others are proteins carbohydrates and lipids. It s sugar is linked to a phosphate group at one end nitrogenous base at other end.
The backbones of both substances consist of alternating molecules of phosphate and sugar. Both dna and rna.
Https Www Freemansd Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 1777 Dataid 5586 Filename Unit 202 20notes Pdf
 Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica
Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica
 Nucleic Acids Dna And Rna A Level Biology Revision Notes
Nucleic Acids Dna And Rna A Level Biology Revision Notes
D1 Origins Of Life On Earth Bioninja
 Life S First Molecule Was Protein Not Rna New Model Suggests
Life S First Molecule Was Protein Not Rna New Model Suggests
Dna And Rna Introduction To Chemistry
 Unit 3 A Guided Reading On Macromolecules With Nnhsbergbio
Unit 3 A Guided Reading On Macromolecules With Nnhsbergbio
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gctlxfutzkajaqeq2kf2eskj Qz17uag357ocqzyer1ft 2ii8ms Usqp Cau
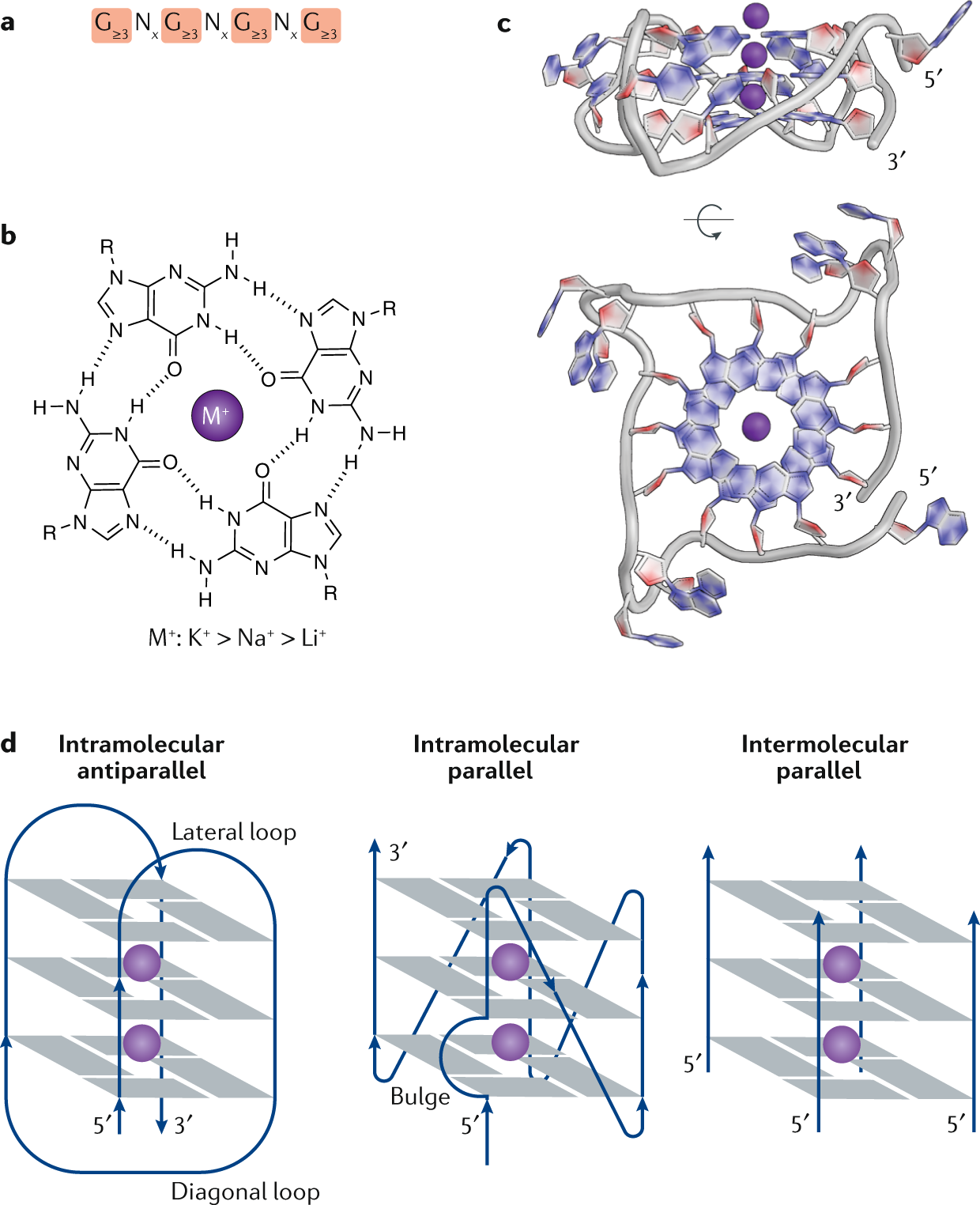 The Regulation And Functions Of Dna And Rna G Quadruplexes
The Regulation And Functions Of Dna And Rna G Quadruplexes
 Organic Vs Inorganic Molecules Flashcards Quizlet
Organic Vs Inorganic Molecules Flashcards Quizlet
Https Www Austincc Edu Tav 1408adobe 1408biochemistry Pdf
 Nucleic Acids Dna Rna Ppt Download
Nucleic Acids Dna Rna Ppt Download
D1 Origins Of Life On Earth Bioninja
 What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io
What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io
 Dna Structure And Function Biology I Laboratory Manual
Dna Structure And Function Biology I Laboratory Manual
 Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica
Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica
/DNAstructure-58c233583df78c353c23dbe6.jpg) Nucleic Acids Function Examples And Monomers
Nucleic Acids Function Examples And Monomers
 Building Blocks Of Dna And Rna Could Have Appeared Together Before
Building Blocks Of Dna And Rna Could Have Appeared Together Before
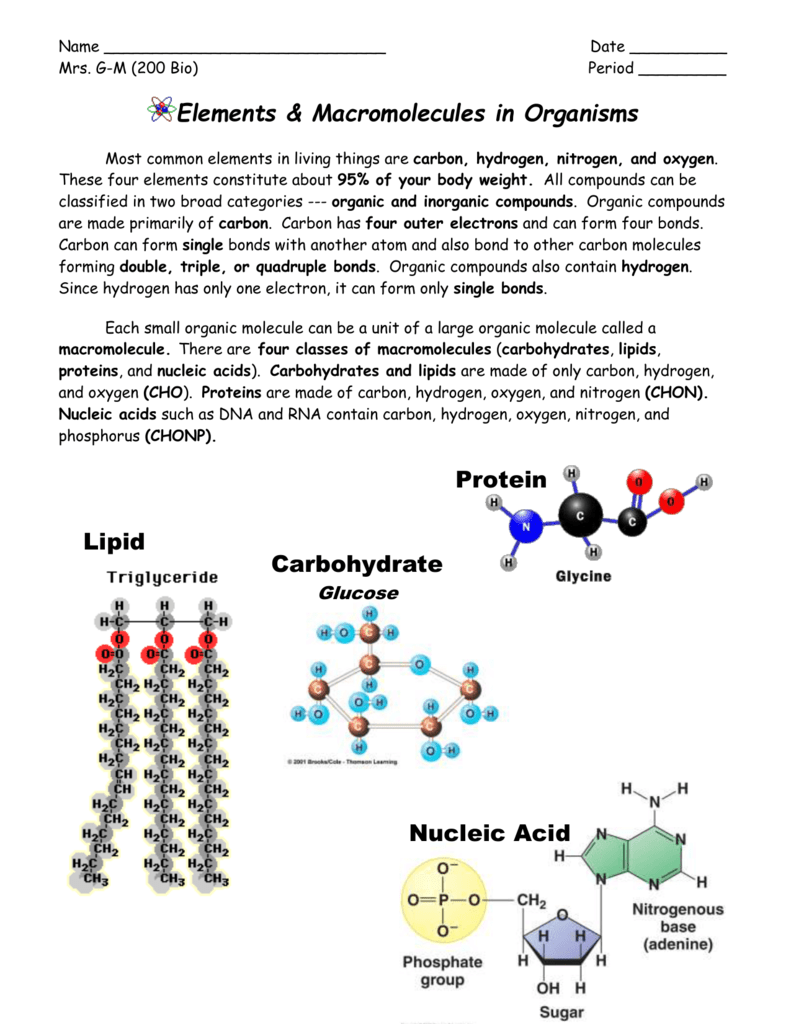 Nucleic Acids Mrs Gm Biology 200
Nucleic Acids Mrs Gm Biology 200
 Major Elements In Biological Molecules Proteins Nucleic Acids
Major Elements In Biological Molecules Proteins Nucleic Acids
 Organic Compounds Compounds That Contain Carbon Hydrogen And Or
Organic Compounds Compounds That Contain Carbon Hydrogen And Or
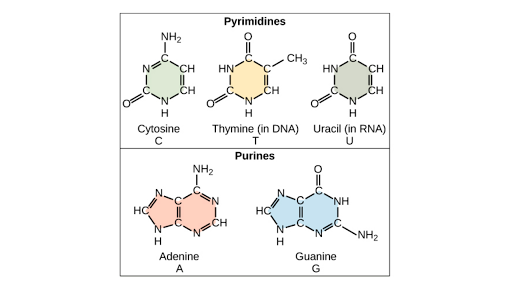
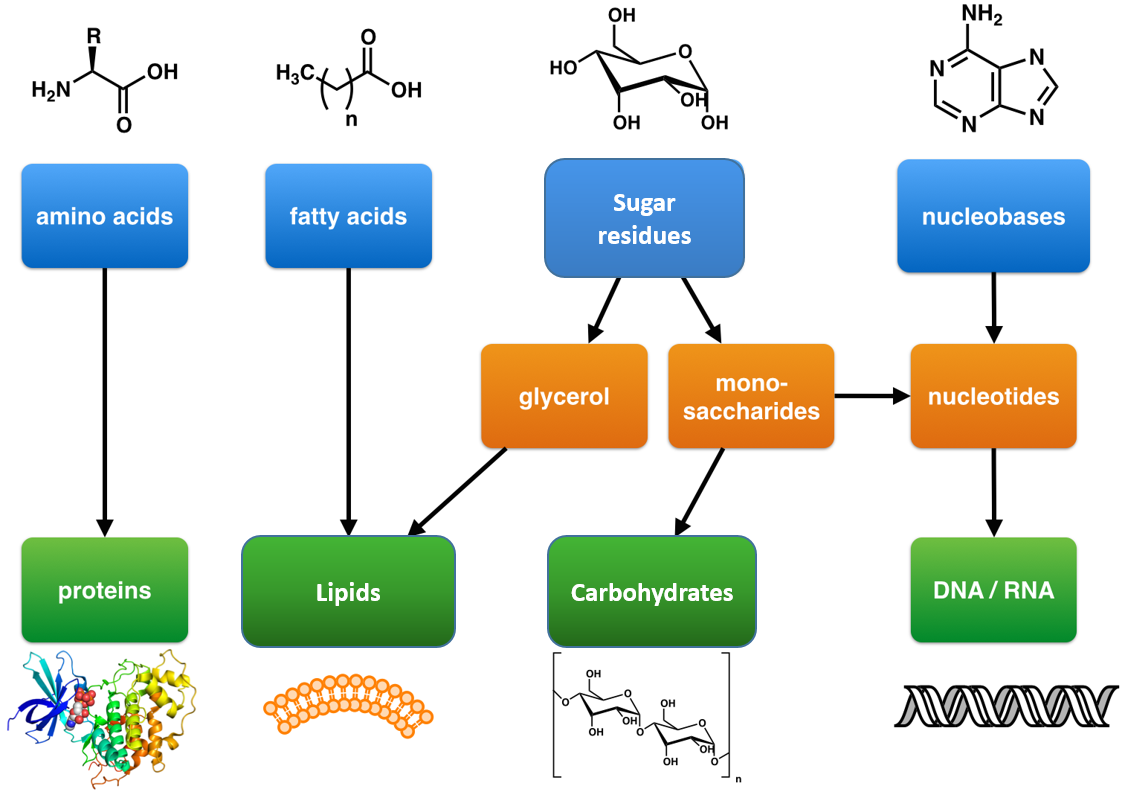 Ch103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
Ch103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
 Chemistry Ii Water And Organic Molecules
Chemistry Ii Water And Organic Molecules
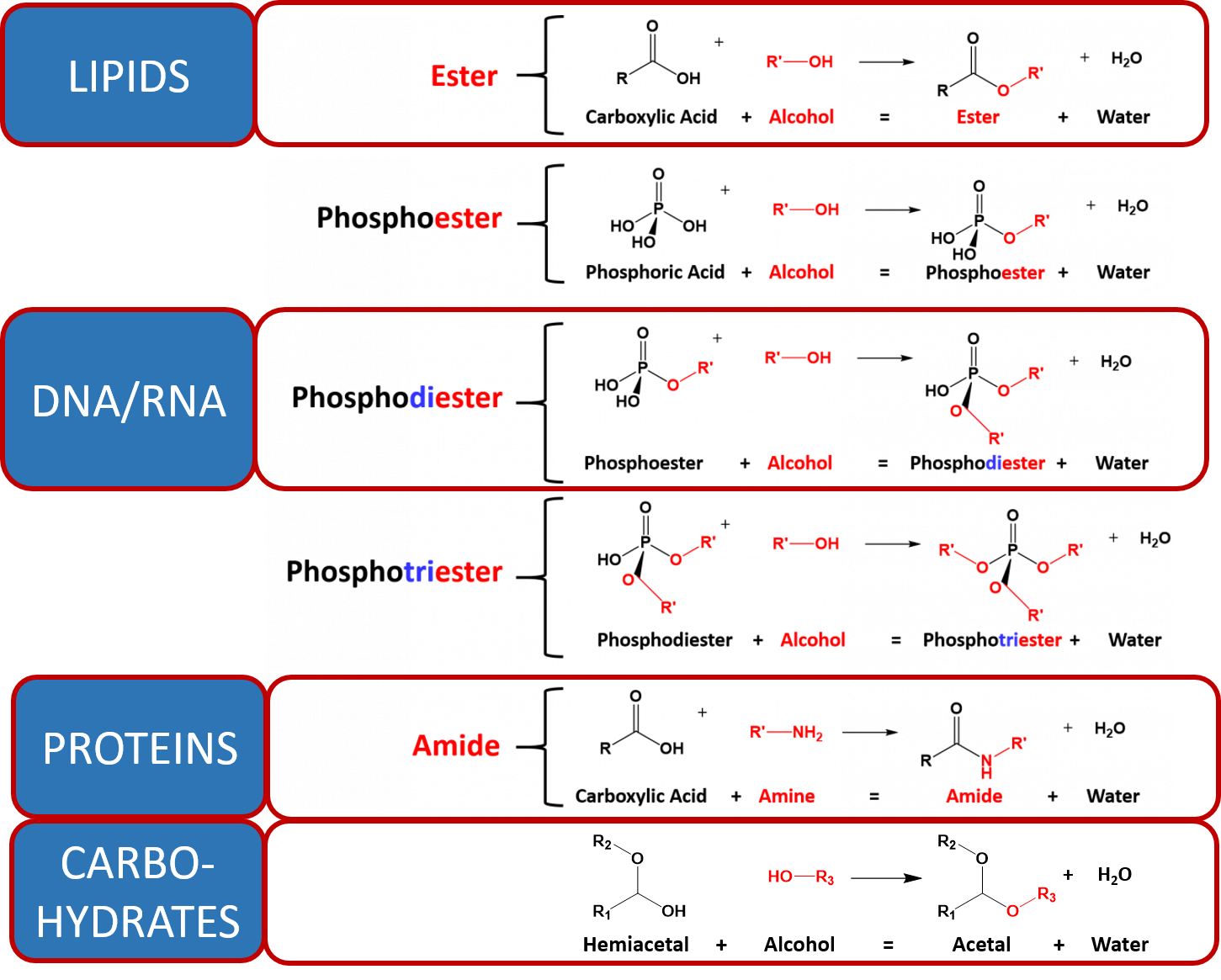 Ch103 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions In Biological Systems
Ch103 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions In Biological Systems
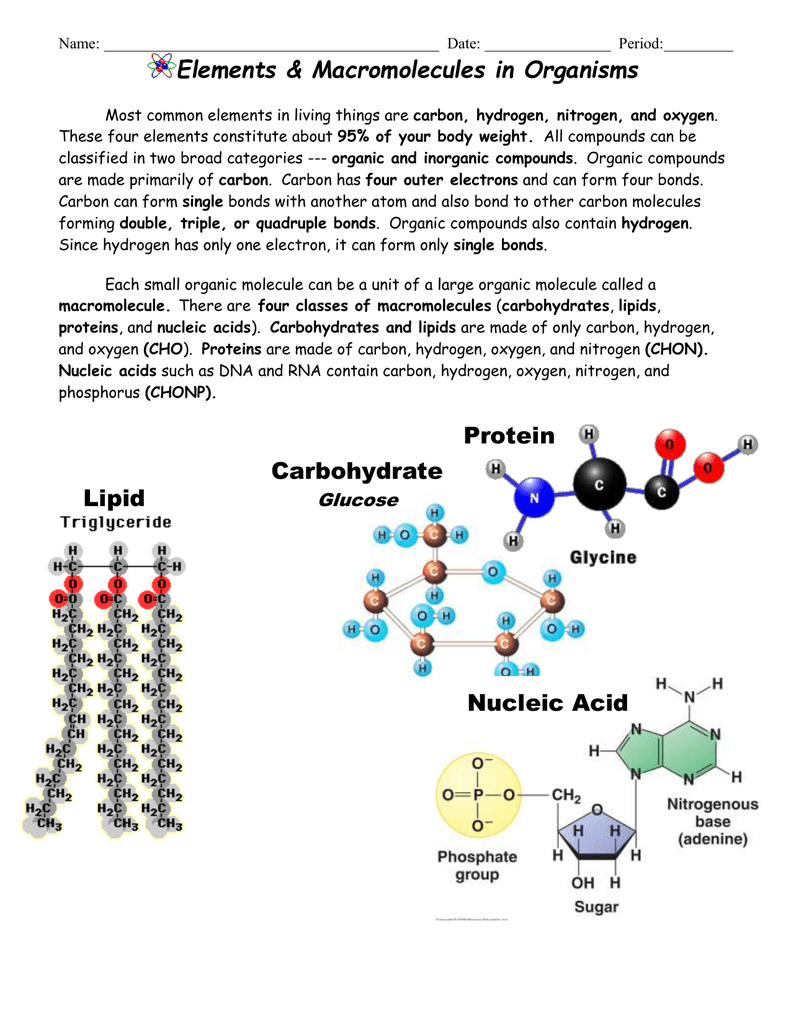 Elements Found In Living Things
Elements Found In Living Things
 What Is The Function Of Dna What Does Dna Do Ancestrydna
What Is The Function Of Dna What Does Dna Do Ancestrydna
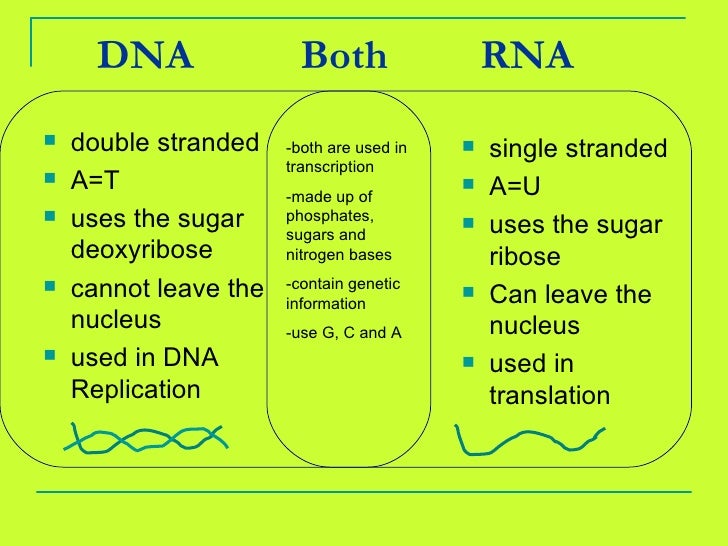



Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar