Sub Cortical White Matter
Magnetic resonance imaging can be used to diagnose various ailments of the brain from dementia to tumors this diagnostic tool can identify gray matter and white matter hyperintensity that could indicate deeper problems. White matter hyperintensities wmhs are lesions in the brain that show up as areas of increased brightness when visualised by t2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging mri.
How often have you read there are small scattered foci of signal abnormalities t2 hyperintensities or increased flair signal in the cerebral white matter indicative of demyelinating disease chronic white matter ischemia due to microvascular disease or gliosis from an infectious inflammatory disease process or words just like them in your mri reports of your elderly patients with.

Sub cortical white matter. Lesions which are identified through imaging may lead to a disconnect between certain regions of the brain thereby creating. Regions of the brain are categorized by color white matter or grey matter and location cortical or related to the cortex subcortical or below the cortex etc the statement therefore means. We often see nonspecific white matter changes hopefully just related to history of htn.
These fibers are coated with a protein called myelin which assists in transmission of electrical impulses down the fibers. The skin is analogous to the cerebral cortex the fleshy part is the deep white matter and the stone represents the subcortical structures. 06 july 2020.
Periventricular white matter disease is not actually a disease. Send thanks to the doctor. Subcortical white matter often simply called white matter is a region inside the brain that has a high concentration of nerve fibers.
Dan harkins last modified date. Cortical dementia is typically associated with the brain s gray matter. 01 july 2020.
Subcortical structures are a group of diverse neural formations deep within the brain which include the diencephalon pituitary. The prevailing view is that these intensities are a marker of small vessel vascular disease and in clinical practice are. Subcortical dementia defined as the term suggests these are dementias believed to initially affect structures below the cortex sub means below and are more associated with the brain s white matter.
The nerve fibers are not interrupted by cell bodies very often so electrical. When white matter hyperintensity appears it is usually a result of old age indicating a loss of blood flow. If we imagine our brain as a peach on the cross section of that peach we d see the outer skin the flesh and an inner stone.
This misnomer comes from health practitioners referring to it as such but periventricular white matter is commonly occurring on the brain and changes in this matter are common as people age 1. Possiblities mini strokes vasculaties ms. This tissue contains millions of nerve fibers or.
Jessica susan reuter last modified date. Wmh s are also referred to as leukoaraiosis and are often found in ct or mri s of older patients. A 48 year old female asked.
Tiny nonspecific periventricular and subcortical white matter. White matter disease is the wearing away of tissue in the largest and deepest part of your brain that has a number of causes including aging.
 Non Active Ms Plaque In Subcortical White Matter In Parietal Lobe
Non Active Ms Plaque In Subcortical White Matter In Parietal Lobe
Relative Decrease In Signal Intensity Of Subcortical White Matter
 Periventricular White Matter Changes Leukoaryosis
Periventricular White Matter Changes Leukoaryosis
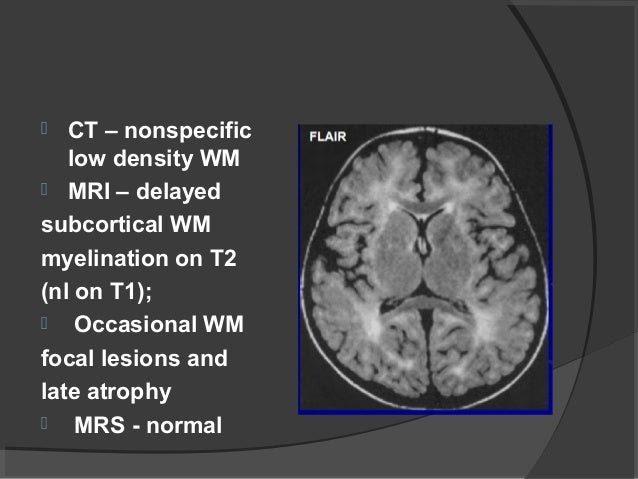 Imaging Of White Matter Diseases
Imaging Of White Matter Diseases
 Subcortical White Matter Pt 4 Cortex Coursera
Subcortical White Matter Pt 4 Cortex Coursera
 Vicente Martin On Twitter Type 2a Confluent Cytotoxic Edema In
Vicente Martin On Twitter Type 2a Confluent Cytotoxic Edema In
 White Matter Hyperintensities On Mri Artefact Or Something Sinister
White Matter Hyperintensities On Mri Artefact Or Something Sinister
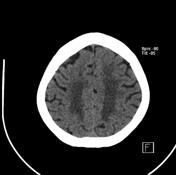 Leukoaraiosis Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Leukoaraiosis Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
 Mri Scan Showing Bright Subcortical White Matter Changes
Mri Scan Showing Bright Subcortical White Matter Changes
 Micro Vascular Diseases Of White Matter
Micro Vascular Diseases Of White Matter
Hyperintensity Of The Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter
Diagnostic Imaging Of White Matter Abnormalities Congenital
 Clinical Characteristics In Subcortical Ischemic White Matter Disease
Clinical Characteristics In Subcortical Ischemic White Matter Disease
 A Tiny Active Ms Plaque In Subcortical White Matter In Parietal
A Tiny Active Ms Plaque In Subcortical White Matter In Parietal
 Does A Patient S Blurry Vision Signal A Serious Condition
Does A Patient S Blurry Vision Signal A Serious Condition
 Gray Matter Specific Mr Imaging Improves The Detection Of
Gray Matter Specific Mr Imaging Improves The Detection Of
Amicus Illustration Of Amicus Injury Brain Hyperintensity
 Figure 1 From Periventricular White Matter Hyperintensities
Figure 1 From Periventricular White Matter Hyperintensities
 Frontal Lobe White Matter Hyperintensities And Neurofibrillary
Frontal Lobe White Matter Hyperintensities And Neurofibrillary
Diagnostic Imaging Of White Matter Abnormalities Congenital
 Axial Flair Mri Multifocal Confluent Subcortical White Matter
Axial Flair Mri Multifocal Confluent Subcortical White Matter
 White Matter Hyperintensities On Mri Artefact Or Something Sinister
White Matter Hyperintensities On Mri Artefact Or Something Sinister
 Periventricular White Matter Lesions
Periventricular White Matter Lesions
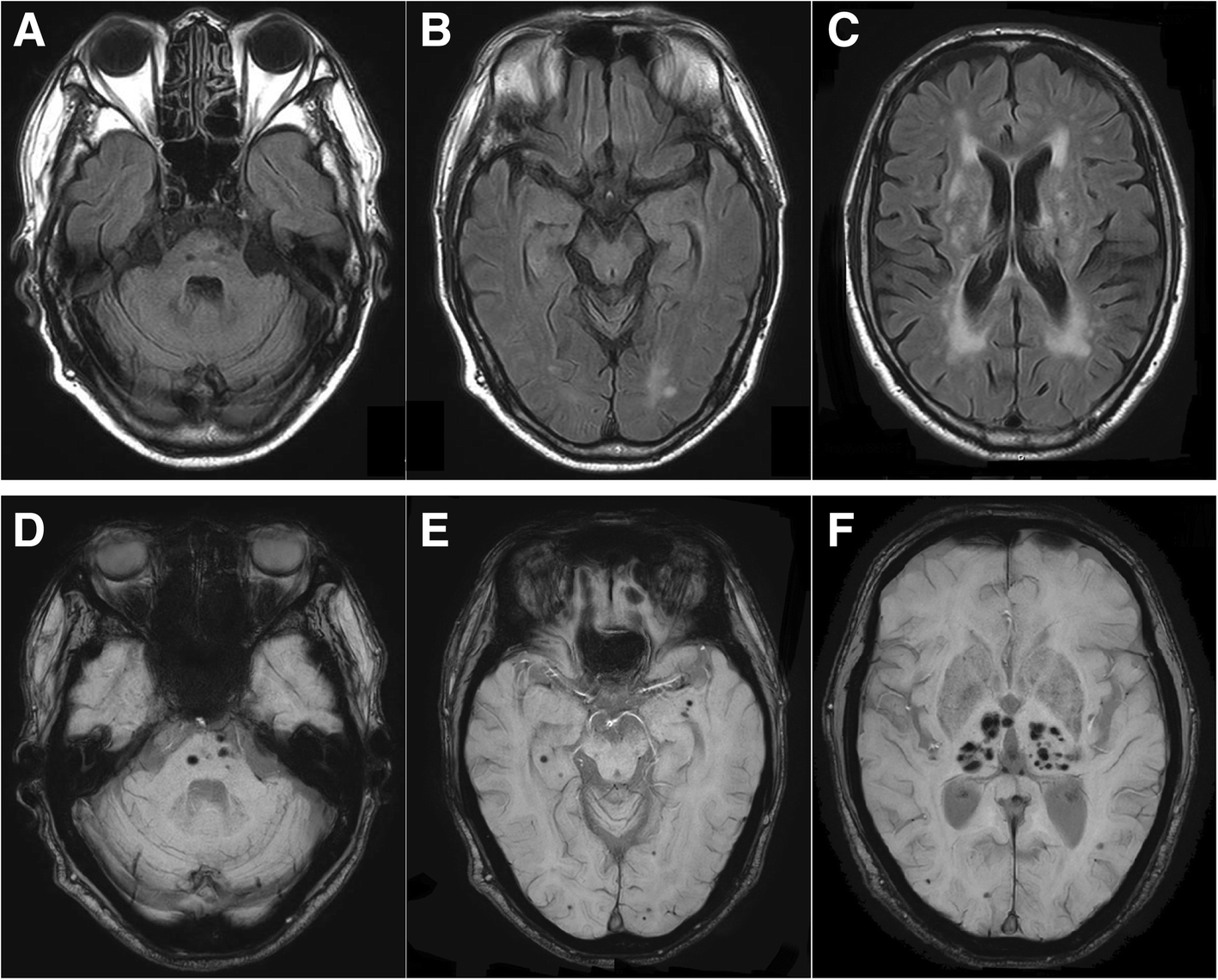 Peripheral Neuropathy In A Case With Cadasil A Case Report Bmc
Peripheral Neuropathy In A Case With Cadasil A Case Report Bmc
 Figure 1 From Subcortical White Matter Lesions In Osmotic
Figure 1 From Subcortical White Matter Lesions In Osmotic
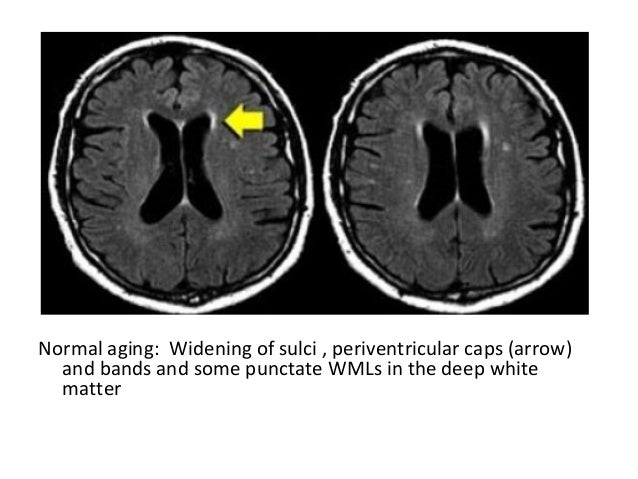 Diagnostic Imaging Of Degenerative White Matter Diseases
Diagnostic Imaging Of Degenerative White Matter Diseases
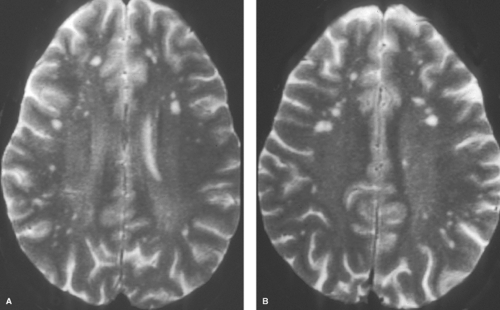 White Matter And Neurodegenerative Diseases Radiology Key
White Matter And Neurodegenerative Diseases Radiology Key
 Periventricular White Matter Lesions
Periventricular White Matter Lesions
 Dr Balaji Anvekar Frcr Frontal Subcortical White Matter Cystic
Dr Balaji Anvekar Frcr Frontal Subcortical White Matter Cystic
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcrgugmvs6pezmhlvzcnvmintmmktkpl9elokrs1qqmmowuxaslj Usqp Cau
 Atrial Fibrillation And White Matter Hyperintensities More Than
Atrial Fibrillation And White Matter Hyperintensities More Than
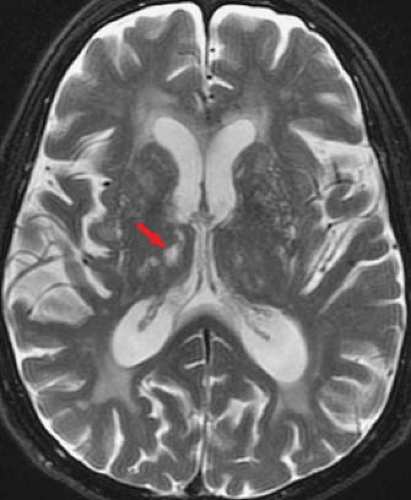 White Matter And Neurodegenerative Diseases Radiology Key
White Matter And Neurodegenerative Diseases Radiology Key
 White Matter Lesions Cognition And Recurrent Hemorrhage In Lobar
White Matter Lesions Cognition And Recurrent Hemorrhage In Lobar
 Periventricular White Matter Lesions
Periventricular White Matter Lesions
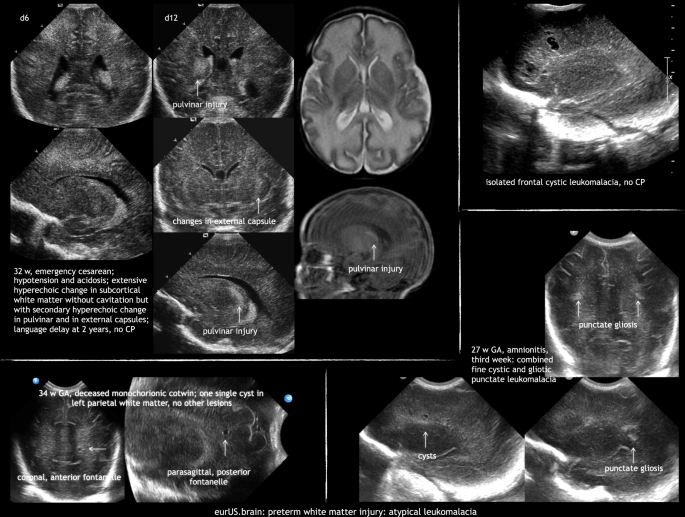 Preterm White Matter Injury Ultrasound Diagnosis And
Preterm White Matter Injury Ultrasound Diagnosis And
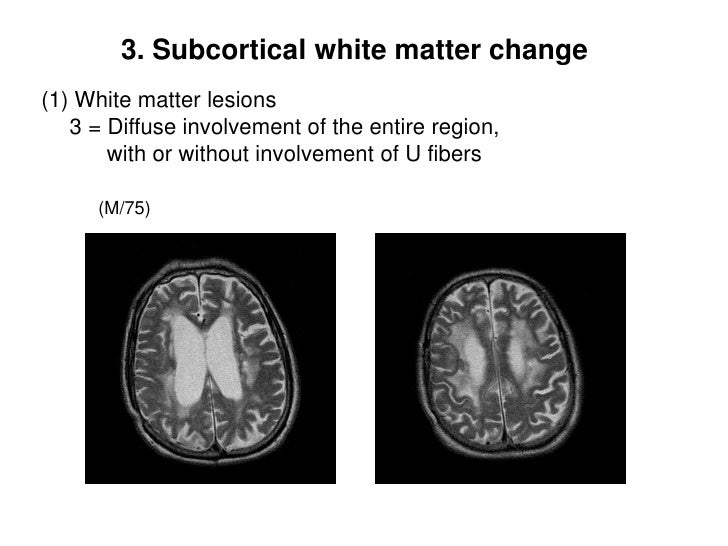 Subcortical Lesion Classification Cnuh Definition 2011 10 10
Subcortical Lesion Classification Cnuh Definition 2011 10 10

Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar